
For a list of BASHing data 2 blog posts see the index page. ![]()
Line spacing tricks - updated
The 3-line file used in this post is called "snip":
aaa
bbb
ccc
The tricks shown in this post are the easiest ones I know. There are other ways to do these jobs on the command line, but they're not so simple. An interesting but not-so-simple AWK command is shown in the Footnote.
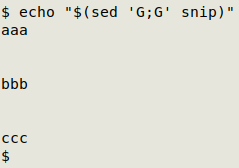
Adding a line space. Adding one blank line between existing lines is "double-spacing" and is most easily done with sed G:
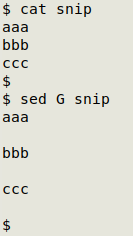
As you can see, sed adds a blank line after every line, including the last. How to delete that trailing blank line? Three easy ways are to delete the last byte (the last newline character) with head, delete the last line with sed, or echo the sed G output:
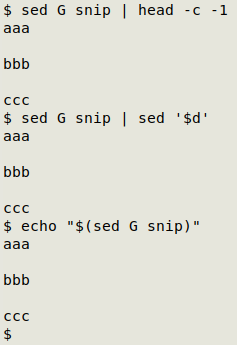
----------------------------------------------------
UPDATE: Reader Tim Chase suggested a better way to add the line spacing with sed, but not after the last line:
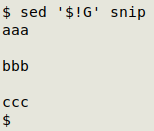
The command sed '$!G' applies the "G" command to all lines that are not (!) the last line ($). In the screenshot below I'm adding a line space to lines that aren't line 2:
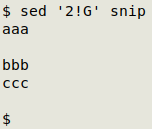
The same idea works with adding multiple line spaces (next section of this post), for example:
sed '$!{G;G;G;}' snip
----------------------------------------------------
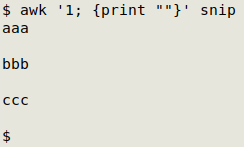
AWK can do double-spacing by printing every line (the default action) and an empty line, but sed G is quicker to type and the AWK command again builds a trailing blank line:
Adding multiple line spaces. Repeating the sed "G" option will do this job easily, as will setting the output record separator (ORS) in AWK to one more than the desired number of newlines. Below, I'm "triple-spacing" — 2 blank lines after every line — and in the AWK command the ORS is set in a "pseudo-argument":

To delete all trailing blank lines simply, I'd use echo; for example:
Removing line spaces. To delete all genuinely blank lines, the two easiest commands to use are awk NF and grep:

To replace multiple blank lines with a single blank line, the simplest command is cat -s:

Footnote
This AWK command can do double- or triple-spacing without trailing blank lines:
awk -v ORS="\n\n" 'NR>1 {print x} {x=$0} END {printf("%s\n",$0)}' snip
awk -v ORS="\n\n\n" 'NR>1 {print x} {x=$0} END {printf("%s\n",$0)}' snip

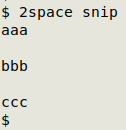
The command can be saved as a function, for example
2space() { awk -v ORS="\n\n" 'NR>1 {print x} {x=$0} END {printf("%s\n",$0)}' "$1"; }
Last update: 2024-09-03
The blog posts on this website are licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License