
For a full list of BASHing data blog posts, see the index page. ![]()
Changing the month format: a fairly general solution
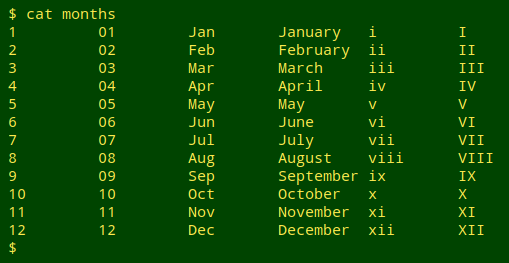
I sometimes need to change the month format in a dataset, for instance from "Jan" to "01", or "3" to "March". There are various clever ways to do this on the command line, but I'm not good at remembering clever. To save time I wrote a table with the 6 different month formats I see most often. It's the table you see below, and if you highlight and copy it, you should be able to paste it into a text editor as a tab-separated table. Save the file as "months".
| 1 | 01 | Jan | January | i | I |
| 2 | 02 | Feb | February | ii | II |
| 3 | 03 | Mar | March | iii | III |
| 4 | 04 | Apr | April | iv | IV |
| 5 | 05 | May | May | v | V |
| 6 | 06 | Jun | June | vi | VI |
| 7 | 07 | Jul | July | vii | VII |
| 8 | 08 | Aug | August | viii | VIII |
| 9 | 09 | Sep | September | ix | IX |
| 10 | 10 | Oct | October | x | X |
| 11 | 11 | Nov | November | xi | XI |
| 12 | 12 | Dec | December | xii | XII |
My general strategy is to use AWK to change formats, and to load "months" into an appropriate array in the AWK command. Below are a few examples.
"months" is always in the working directory, and my data files are always tab-separated.
Expand abbreviated month
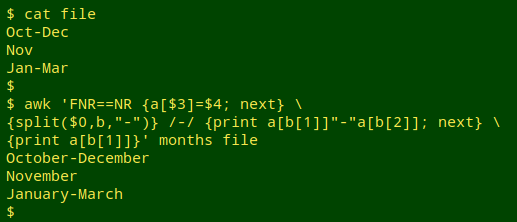
awk 'FNR==NR {a[$3]=$4; next} {split($0,b,"-")} /-/ {print a[b[1]]"-"a[b[2]]; next} {print a[b[1]]}' months file
Split "full" date into ISO 8601 components
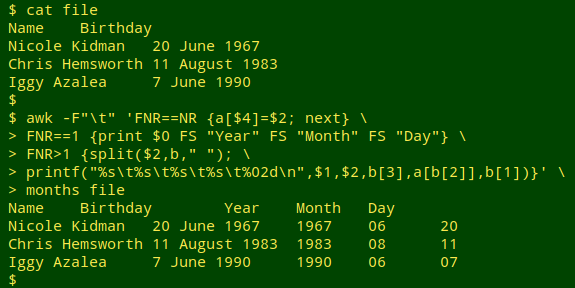
awk -F"\t" 'FNR==NR {a[$4]=$2; next} FNR==1 {print $0 FS "Year" FS "Month" FS "Day"} FNR>1 {split($2,b," "); printf("%s\t%s\t%s\t%s\t%02d\n",$1,$2,b[3],a[b[2]],b[1])}' months file
Convert "full American" date into Roman month-numeral date
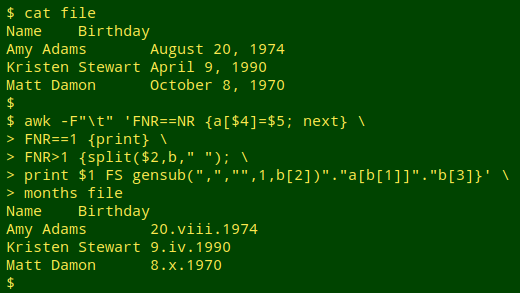
awk -F"\t" 'FNR==NR {a[$4]=$5; next} FNR==1 {print} FNR>1 {split($2,b," "); print $1 FS gensub(",","",1,b[2])"."a[b[1]]"."b[3]}' months file
Convert date range into ISO 8601 interval date
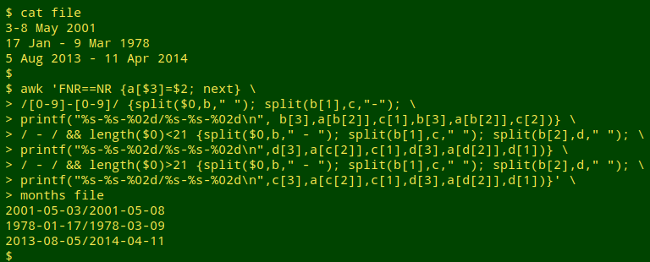
awk 'FNR==NR {a[$3]=$2; next} /[0-9]-[0-9]/ {split($0,b," "); split(b[1],c,"-"); printf("%s-%s-%02d/%s-%s-%02d\n", b[3],a[b[2]],c[1],b[3],a[b[2]],c[2])} / - / && length($0)<21 {split($0,b," - "); split(b[1],c," "); split(b[2],d," "); printf("%s-%s-%02d/%s-%s-%02d\n",d[3],a[c[2]],c[1],d[3],a[d[2]],d[1])} / - / && length($0)>21 {split($0,b," - "); split(b[1],c," "); split(b[2],d," "); printf("%s-%s-%02d/%s-%s-%02d\n",c[3],a[c[2]],c[1],d[3],a[d[2]],d[1])}' months file
For more on splitting again the split-out parts of a string, see this BASHing data post.
To remind myself which fields are which in "months", I just cat the file before building the AWK command:
Last update: 2018-12-30
The blog posts on this website are licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License